DTS: PipeLine 만들고 활용하기
§ 다음 posting
☞ PipeLine
sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline
class sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline(steps, *, memory=None, verbose=False)
data : ref
Model을 바로 확인 하기 어렵다.
과대적합 하는지 확인 하기 위해 pipeLine을 이용하여 쉽게 파악 할 수 있다.
mlops? 때문이다.
- pipeLine : 최종 추정을 위한 변환 파이프라인
- 매개변수를 바꿔가며 교차 검증 할 수 있는 여러 단계를 묶어 놓아 하나의 함수로 만들어 사용하기 쉽게 한 것.
- 해당 이름의 매개 변수를
chaining estimators 을 위해 설정하거나,
제거 할 수 있다.- convenience and encapsulation
- joint parameter selection
- safety
뭘 한건지 모르겠지만, 오늘 할 것 정리 해 보자 .
1 | import pandas as pd |
- 일단 sklearn을 이용한 ML을 하기 위해 library를 import 해 보자.
data 불러오기
1 | data_url = 'https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/wdbc.data' |
test, Train 나누기
1 | X = df.loc[:, "radius_mean":].values |
이 코드 하나가 pipe Line
- LogisticRegression
1 | from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression |
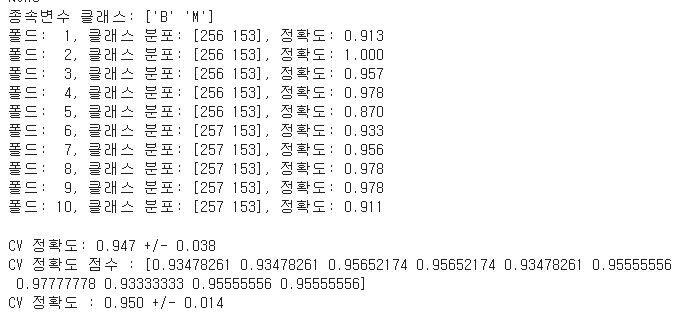
- DecisionTreeClassifier
1 | from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier |
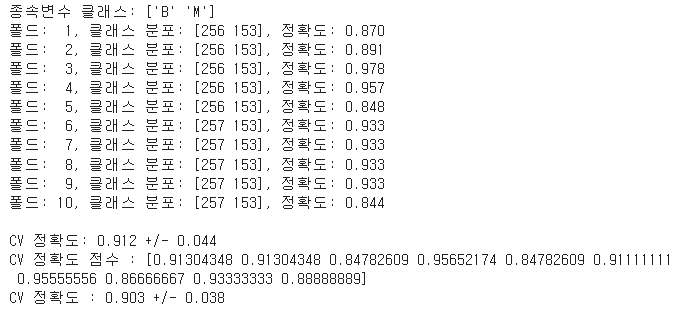
- LGBM
1 | from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier |
LGBMC : 이거 아닌거같은데 못봤다. 안됨 여튼
이런식으로 바꿔 끼워가며 확인 할 수 있다.
pipeLine만들기
1 | from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression |
- Kaggle data랑 뭐가 다른지 확인 해 보라고 하는데
- Kaggle에서 어디 있는지 잘 모르겠다.
- 자바는 어느정도 감이 왔는데 python은 당최 아얘 감조차 안온다.
- 그냥 python 강의나 들어야 하나 고민중 …